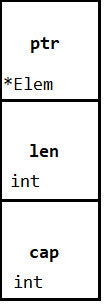
slice 表示底层数组的一个分片,内部数据结构包含三个字段:指向底层数组的指针 (ptr)、数组分片的长度 (len) 和底层数组大小 (cap) ,示意图如下:
1. 初步了解
首先通过变量声明来认识下 nil slice 和 empty slice:
var s []int // 【1】
var t = []int{} // 【2】
fmt.Printf("value of s: %#v\n", s)
fmt.Printf("value of t: %#v\n", t)
/* output
// value of s: []int(nil)
// value of t: []int{}
*/
语句【1】声明了一个[]int类型的变量, 其值为[]int(nil),这就是 nil slice,表示 slice 类型的 zero value。
语句【2】声明并定义了一个[]int类型的变量,其值为[]int{},这就是 empty slice。
fmt.Printf("s: len=%d, cap=%d\n", len(s), cap(s)) // 【3】
fmt.Printf("t: len=%d, cap=%d\n", len(t), cap(t)) // 【4】
/* output
// s: len=0, cap=0
// t: len=0, cap=0
*/
从语句【3】和【4】输出结果来看,这两种 slice 的 len 和 cap 字段值都为0。
接下来将它们分别和nil进行比较:
fmt.Printf("s is nil? %v\n", s == nil) // 【5】
fmt.Printf("t is nil? %v\n", t == nil) // 【6】
/* output
// s is nil? true
// t is nil? false
*/
语句【5】和【6】输出结果表明 nil slice 的值等于 nil,而 empty slice 则不等于。
2. 数据结构
再看下这两种 slice 内部数据结构的表示:
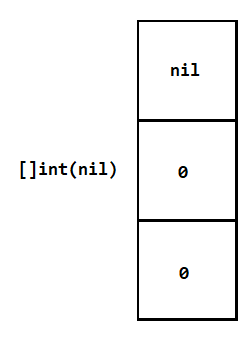
- nil slice 数据结构示意图
- empty slice 数据结构示意图
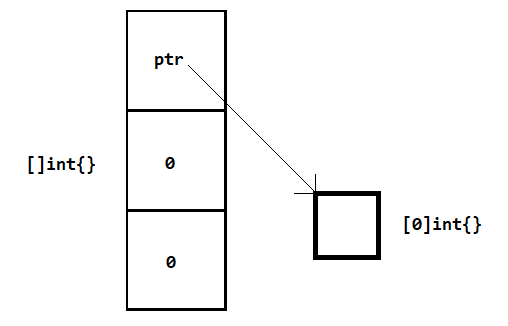
nil slice 没有底层数组(ptr 指针为 nil),empty slice 有底层数组,不过数组大小是 0 。
3. 习惯用法
nil slice 常用来表示 slice 不存在,如实现一个要求返回 slice 类型的函数,当执行流程出现异常,可以提前返回一个 nil slice 和 error。
empty slice 常用来表示空集合,如用来表示 db 查询返回的结果集为空。
多数情况下,两种 slice 可以相互替换,但有些使用场景需要注意区分,比如对 JSON 对象进行编码。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"encoding/json"
)
type A struct {
Data []string
}
func main() {
var nilSlice []string
var emptySlice = []string{}
b, _ := json.Marshal(A{nilSlice})
fmt.Printf("%s\n", b)
b, _ = json.Marshal(A{emptySlice})
fmt.Printf("%s\n", b)
/* output
// {"Data":null}
// {"Data":[]}
*/
}
nil slice 被编码成 null,而 empty slice 被编码成 [],在设计 API 时要注意这点,前端需要进行不同的处理。
4. 参考文档
(1) Go Slices: usage and internals
(2) Go: Empty slice vs. nil slice
